Essential Question: How can we investigate for the existence of bacteria, parasites, and other microorganisms in our water?
Lesson Summary: Students learned the art of observation and first practiced this new skill on a set of videos of pond microorganisms. Next students used microscopes to observe microorganisms in pond water from Central Park. Using a digital microscope we were able to capture some of the creatures we found. Let's just say I don't think any AMS scholars or faculty will be swimming in ponds anytime soon after this lab.

Essential Question: How can we determine if water is too contaminated to drink?
Lesson Summary:
In part 1 of the laboratory procedure we tested the pH( a measure of acidity) for eight different beverages. The lower the pH the more acidic the substance. The higher the pH, the more basic a substance is. The scale ranges from 1 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Students found neutral pHs for water fountain water, milk, fiji, and poland spring. Coke and vitamin water were highly acidic and possibly dangerous and could possibly lead to health problems by disrupting pH homeostasis in the body.
For part 2 each lab group used a water testing kit to record levels of copper, iron, chlorine, nitrogen, and hardness in the water. The class concluded that the low level of contaminants in the water fountain water was safe enough to drink. Alternatively, the high levels of nitrogen in the compost water was dangerous to consume.
Essential Question: How can we purify water from a filthy source to make it drinkable?
Lesson Summary: In this lesson students explored the purification process that transforms compost water into drinking water.
We learned about five different stages in the purification process:
1. Aeration
2. Coagulation
3. Sedimentation
4. Filtration
5. Disinfection
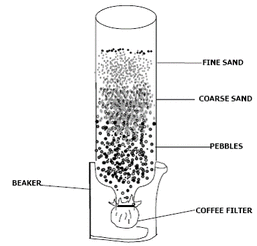
After expert testimony from students, the class participated in a filtration demo with rocks, sand, and a coffee filter attached to a bottle. Together we successfully (...sort of) filtered compost water into only slightly contaminated water.
Demo setup
Waste water treatment video from class
Another from of purification, solar distillation, as shown by Bear Grylls from Man vs. Wild as he distills his own pee.

Essential Question:
How can we determine which type of water students prefer without experimental bias?
Lesson Summary:
Today students were challenged to create their own blind taste test to compare different types of bottled water to the school water fountain water.
The results were quite interesting.
Several groups found that students preferences changed once they could not see the label of the water and concluded that there was experimental bias.
Other students reported in poster presentations that their preferences stayed the same during both rounds of testing.


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed